The future of construction is currently being shaped by a novel manufacturing method: 3D printing. This technology, which first appeared in the 1980s, has made significant strides over the last few decades, and its potential applications in construction are growing every day. More than just a fascinating piece of technology, 3D printing is set to revolutionise the construction industry, providing a more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective approach to building.
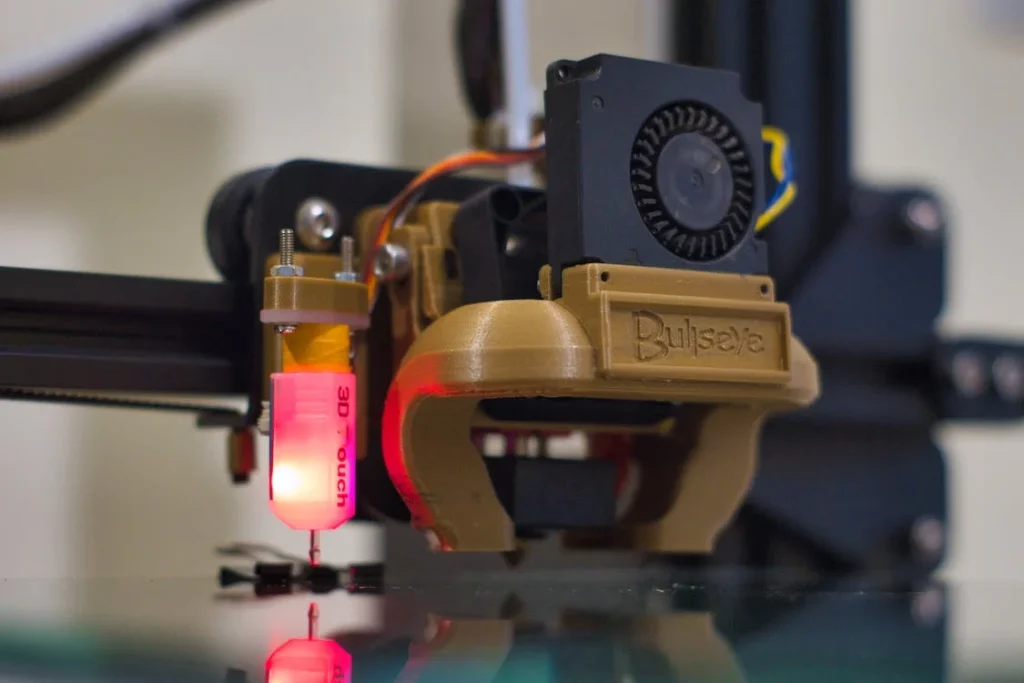

The Concept of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a technology that fabricates three-dimensional objects by depositing materials layer by layer according to a digital model. When applied to construction, a 3D printer, often a robotic arm or a gantry-type unit, extrudes a construction material—commonly concrete—to create structural components or even entire buildings.
The process begins with a digital design created using a computer-aided design (CAD) program. The design is then sliced into thin, horizontal layers that the printer will sequentially lay down. This layer-by-layer approach allows for an incredible level of precision, creating structures that traditional construction methods might find challenging to replicate.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Construction
Increased Efficiency
One of the most appealing advantages of 3D printing is its potential for increased efficiency. Traditional construction processes involve multiple stages, from the initial site preparation to the building and finishing stages, each with a potential for delays and inefficiencies. With 3D printing, many of these stages can be consolidated and streamlined. Construction speed can be significantly increased, reducing the building time from months to mere days in some cases.
Cost Reduction
3D printing also has the potential to significantly reduce costs. Labour costs can be reduced as fewer workers are needed on-site, and the risk of accidents is also minimized. Material costs can be decreased, as 3D printing requires fewer resources and generates less waste.
Design Flexibility
The level of design flexibility and customization achievable with 3D printing is unmatched. Because the technology relies on digital models, it allows architects and engineers to move beyond the limitations of traditional construction, creating complex shapes and structures with ease. This gives rise to innovative architectural designs that were once considered impractical or even impossible.
Environmental Sustainability
3D printing can contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. It significantly reduces material waste compared to conventional construction methods, as the exact amount of material needed can be precisely calculated and used. Additionally, 3D printers can use recycled materials, further reducing environmental impact. Lastly, by reducing the need for transportation and heavy machinery, 3D printing can contribute to lower CO2 emissions.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
The use of 3D printing in construction is not a distant prospect; it’s happening right now. Several companies worldwide have successfully used 3D printers to create residential homes, commercial buildings, and even bridges.
For instance, in 2020, a company named COBOD printed a two-story building in Germany in just a few weeks. In the Netherlands, the Project Milestone initiative successfully built the first of five planned 3D printed concrete houses. And in China, WinSun made headlines when they managed to print ten houses in just 24 hours.
The Future of 3D Printing in Construction
As with any innovative technology, there are challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. Regulatory hurdles, technological limitations, and the need for skilled operators are just a few of the obstacles that 3D printing faces. However, with continuous advancements and increasing interest from the construction industry, these hurdles are becoming less daunting.
In the near future, we may see a greater blend of traditional construction methods with 3D printing. It’s also likely that we’ll see more widespread use of different materials in 3D printing, such as metals, polymers, and advanced composites, opening up new avenues for innovation and design.
The potential applications are vast. From low-cost housing solutions and disaster relief structures to ambitious off-world construction projects for future lunar or Martian bases, the possibilities for 3D printing in construction are as exciting as they are endless.
Undoubtedly, 3D printing is set to revolutionise the construction industry. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of transforming the way we design, build, and think about our built environment.
Pushing Boundaries: Large Scale 3D Printing and Infrastructure
As 3D printing technology advances, so does the scale of its potential applications. Large-scale 3D printing, sometimes referred to as ‘contour crafting’, is the frontier where construction and advanced manufacturing technologies meet. This revolutionary application has the potential to construct larger structures such as bridges, commercial buildings, and even skyscrapers.
A remarkable example of this is the 3D-printed concrete bridge in the town of Gemert, the Netherlands. The bridge, which is used by cyclists, was printed by the Eindhoven University of Technology in collaboration with several construction companies. What is significant about this project is not only the technology but also the process. The components of the bridge were printed at the university and then transported and assembled at the site. This off-site construction method reduces potential disruption at the construction site and shortens construction timelines significantly.
The Impact of 3D Printing on the Construction Workforce
While 3D printing in construction presents numerous benefits, it’s also essential to consider its impact on the construction workforce. The technology could lead to labour-saving efficiencies, but this could also mean job displacement for some roles traditionally done by manual labour. On the other hand, new jobs will likely be created in areas such as machine operation, maintenance, and digital design.
The shift will necessitate construction professionals to upskill and adapt to new technologies, emphasising the need for ongoing education and training within the industry. The rise of 3D printing, like any disruptive technology, underlines the importance of adaptability and lifelong learning in the construction industry.

Standardisation and Regulations
As with any new technology, especially one with the potential to create significant change, standards and regulations are crucial. As the industry begins to adopt 3D printing more widely, the need for regulatory frameworks and standards becomes increasingly evident. These will address the durability, safety, and quality of 3D printed structures, among other issues.
Organisations like ASTM International and ISO are already working towards the development of standards for additive manufacturing, including 3D printing in construction. As we move forward, ensuring that these guidelines are implemented and adhered to will be a critical aspect of the successful adoption of 3D printing technology.
Further Applications of 3D Printing in Construction
While the earlier sections touched upon the various facets of 3D printing in construction, it’s worth noting that its potential applications extend beyond creating structures. Indeed, as the technology develops, its versatility continues to unfold.
Disaster Relief and Housing
One application with tremendous potential is the use of 3D printing for rapid disaster relief. Natural disasters often leave people homeless and in desperate need of shelter. Conventionally, providing temporary housing in such situations is a logistical challenge and can take a considerable amount of time. However, 3D printing offers a way to accelerate this process.
By using 3D printers, emergency housing can be constructed quickly, efficiently, and at a lower cost than traditional methods. This capability was demonstrated when a Chinese company named WinSun printed ten houses in a single day using a mixture of cement and construction waste. Such feats not only provide a practical solution to housing problems following disasters but also contribute to sustainability.
Customisation and Design Freedom
Another compelling advantage of 3D printing is the design freedom it affords. Traditional construction methods are often limited in the types of shapes and structures they can produce cost-effectively. However, 3D printing enables the construction of more complex and customised designs at no additional cost.
This opens up new possibilities for architects and designers who are no longer bound by the limitations of traditional construction techniques. Instead, they can push the boundaries of design, creating structures that would have been unthinkable or unfeasible in the past.
Infrastructure and Public Facilities
3D printing also offers potential solutions for public infrastructure and facilities. In recent years, several projects have demonstrated the viability of using 3D printing for infrastructure construction. For instance, a team from Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University successfully printed a concrete bathroom unit in less than a day. The unit was then fitted with interior fixtures and installed at a public park.
Such projects demonstrate that 3D printing can significantly reduce the time and resources required to construct public facilities. This efficiency has immense implications for developing regions where infrastructure development is a priority but resources may be scarce.
Final Thoughts
The advent of 3D printing in construction represents a paradigm shift that is revolutionising the industry. The technology has the potential to address several longstanding issues, including cost inefficiencies, design limitations, and environmental impact. It can also contribute to tackling urgent global problems such as housing shortages and disaster relief.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, adopting these digital innovations will be crucial. Furthermore, to harness the full potential of technologies like 3D printing, a modern approach to project management is essential. That’s where Wunderbuild comes into play.
Wunderbuild’s construction management software enables construction companies to stay on top of their projects, keeping track of progress in real-time, and managing resources efficiently. With its intuitive design and robust features, Wunderbuild simplifies construction management, allowing you to focus on what matters most – building the future. Discover more about how Wunderbuild can facilitate your construction process here.